Simon Says Game
A tutorial on creating a Simon Says game using the Raspberry Pi Pico
Introduction
In this tutorial, we will create a fun and interactive Simon Says game using the Raspberry Pi Pico microcontroller. This classic memory game will challenge players to remember and replicate a sequence of LED flashes. Each round, the game will display a new random sequence, increasing the difficulty as the player progresses. This project is perfect for beginners looking to learn about programming microcontrollers, working with LEDs, and handling user input.
We will create the game on breadboard with just a few components.
The image below is the popular Simon Says electronic game you can buy.

Components Needed
To build this Simon Says game, you will need the following components:
| Component | Quantity |
|---|---|
| Raspberry Pi Pico | 1 |
| Micro USB Cable | 1 |
| Breadboard | 1 |
| Wires | Several |
| LEDs (Blue,Green, Yellow and Red) | 1 |
| Passive Buzzer | 1 |
| 4 Push Buttons | 1 |
| 1k Ohm Resistor | 3 |
| 220 Ohm Resistor | 1 |
Software
Thonny IDE: A Python IDE that supports MicroPython, which you will use to write and upload your code to the Pico.
MicroPython Firmware: Make sure your Raspberry Pi Pico has MicroPython installed. You can download it from the official Raspberry Pi website.
If it is your first time using the Raspberry Pi Pico, head on over to the Introduction section to learn how to setup the Pico with MicroPython
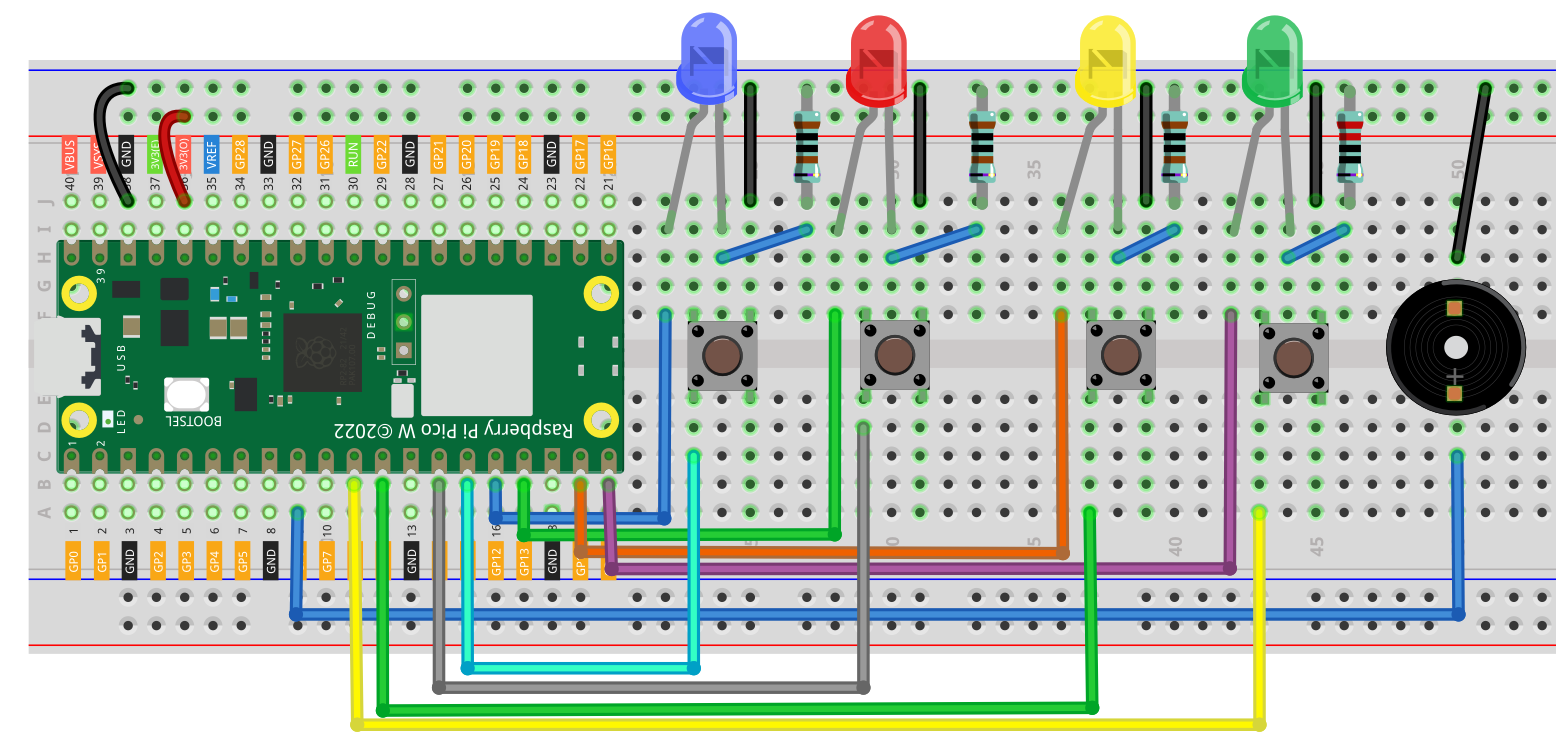
Schematic Diagram
Below is the wire diagram for the simon says game
Code:
Main
import machine
import time
import random
# Define GPIO pins for LEDs and buttons
LED_PINS = [12, 13, 14, 15] # Blue, Red, Yellow, Green
BUTTON_PINS = [11, 10, 9, 8] # Blue, Red, Yellow, Green
BUZZER_PIN = 6 # Buzzer pin
# Initialize LEDs, buttons, and buzzer
leds = [machine.Pin(pin, machine.Pin.OUT) for pin in LED_PINS]
buttons = [machine.Pin(pin, machine.Pin.IN, machine.Pin.PULL_UP) for pin in BUTTON_PINS]
buzzer = machine.PWM(machine.Pin(BUZZER_PIN))
# Define frequencies for each LED color (in Hz)
FREQUENCIES = [440, 494, 523, 587] # A4, B4, C5, D5
# Game variables
sequence = []
user_input = []
speed = 2 # Start speed
def play_tone(frequency):
buzzer.freq(frequency) # Set frequency
buzzer.duty_u16(512) # Set duty cycle (50% - adjust as needed)
time.sleep(0.2) # Play tone for 0.5 seconds
buzzer.duty_u16(0) # Stop the tone
def light_led(index):
leds[index].on()
play_tone(FREQUENCIES[index]) # Play the corresponding tone
time.sleep(0.05) # LED on for 0.5 seconds
leds[index].off()
time.sleep(0.05) # Short pause between LEDs
def flash_button(index):
# Flash the button LED while pressed
leds[index].on()
play_tone(FREQUENCIES[index]) # Play the corresponding tone when button is pressed
time.sleep(0.05)
leds[index].off()
def get_user_input():
global user_input
user_input = []
while len(user_input) < len(sequence):
for i, button in enumerate(buttons):
if button.value() == 0: # Button is pressed
flash_button(i) # Flash the corresponding LED
user_input.append(i) # Add the index of the pressed button
# Check immediately after each input
if user_input[-1] != sequence[len(user_input) - 1]:
return False # Mistake detected
time.sleep(0.2) # Debounce delay
while button.value() == 0: # Wait for button release
time.sleep(0.1)
return True # Input complete
def check_sequence():
return user_input == sequence
def idle_mode():
while True:
for i in range(len(leds)):
leds[i].on()
time.sleep(0.1) # Shorter delay for idle mode
leds[i].off()
time.sleep(0.1)
# Check for button press to start the game
if any(button.value() == 0 for button in buttons):
break
def game_over():
# Flash all LEDs together for game over
for _ in range(3): # Flash 3 times
for led in leds:
led.on()
play_tone(300) # Play a different tone for game over
time.sleep(0.5)
for led in leds:
led.off()
time.sleep(0.5)
def play_game():
global sequence # Ensure we modify the global sequence
# Reset the sequence at the start of each game
sequence = []
while True:
# Generate a new LED index that is not already in the sequence
next_led = random.randint(0, 3) # Random index for LEDs
sequence.append(next_led)
print("Sequence:", sequence) # Debugging line
# Display the sequence
for led_index in sequence:
light_led(led_index)
time.sleep(0.01)
# Get user input
if not get_user_input(): # Check for mistakes immediately
print("Game Over! You failed.")
game_over() # Flash LEDs for game over
break # Exit game to return to idle mode
print("Correct! Next round.")
# Main loop
while True:
idle_mode() # Start in idle mode
time.sleep(1) # Wait for 1 second before starting the game
play_game() # Start the game when a button is pressed