Binary Clock / Weather Monitor WS2812b Version
YouTube Video
Introduction
In this project we’re upgrading a previous project and building a Binary Clock + Weather Display using the Raspberry Pi Pico W and WS2812B through-hole LEDs — which is a cool and Nerdy way to show the time. Instead of regular digits, this clock shows the hours, minutes, and seconds in binary, with a different color for each section and fully customizable since each LED is addressable. It looks awesome on a desk, and it’s a great conversation starter. The oled display will be used to show weather information of your city.
We are using the Pico W which will receive the:
✅ Accurate time from the internet
✅ Live weather data for your city
This is a perfect little IoT build whether you’re learning MicroPython, teaching students, or just love blinking LEDs as much as I do.
Components
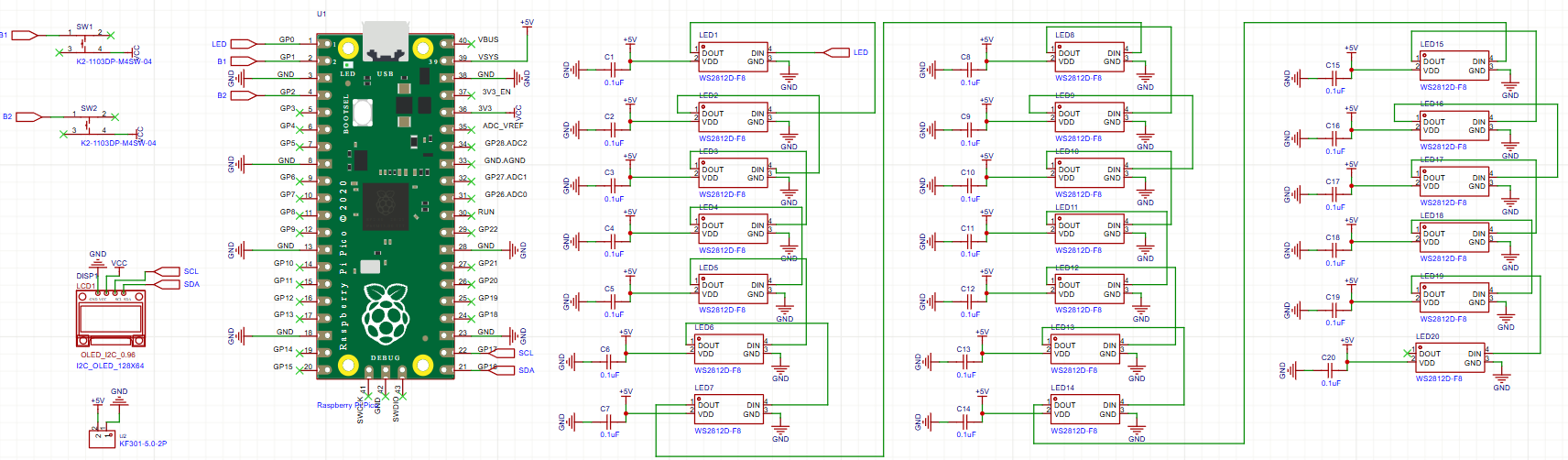
The table below lists all the components required for this project. For the WS2812 4-pin F8 addressable LEDs, please double-check the pinout, as it may vary depending on the manufacturer.
| Component | Quantity |
|---|---|
| Raspberry Pi Pico W | 1 |
| Micro USB Cable | 1 |
| WS2812 4 Pins F8 | 20 |
| 10X10mm Push Buttons | 2 |
| OLED1366 | 1 |
| PCB | 1 |
| 20 Pin Female headers | 1 |
| M3 - 3mm Screws | 4 |
Schematic Diagram
The schematic diagram was created in EasyEDA and can be downloaded here:
PCB Design
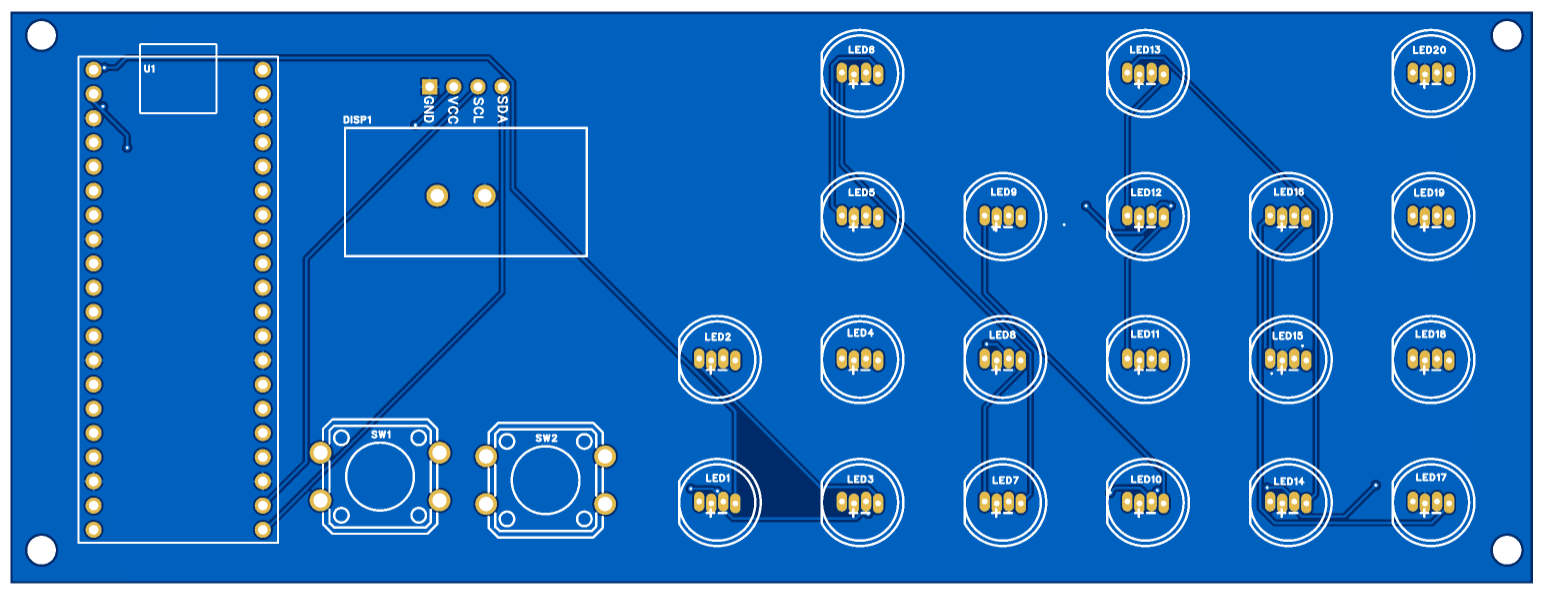
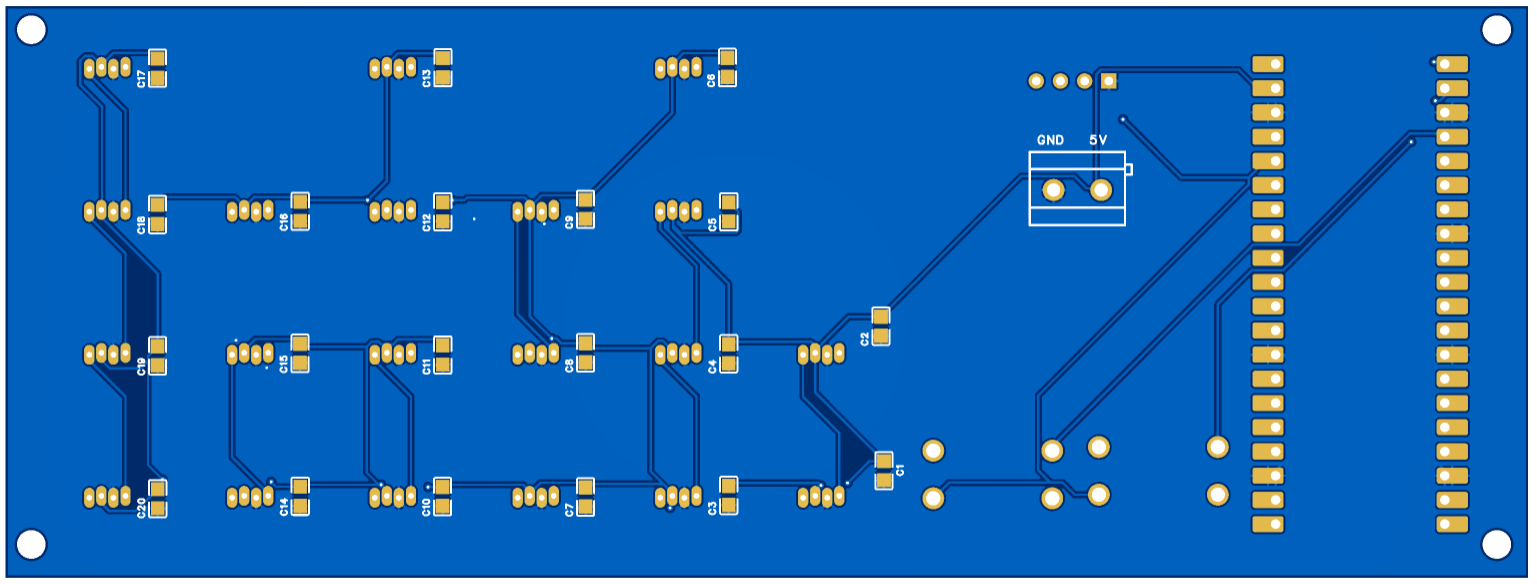
The PCB was designed using EasyEDA, a free and user-friendly web-based tool that supports circuit design, simulation, and PCB layout.
The version in YouTube video has no power input terminal to power Pico from external 5V which I have added in v2.
This design includes several key features:
- Two Push Buttons: These two push buttons will be used to display different data on the OLED display
- Mounting Holes: The PCB is equipped with four 3mm mounting holes, making it easy to secure within an enclosure.
Download Gerber file here: download.
PCB:
Order PCB (JLCPCB)
The PCB was ordered through JLCPCB. They offer great PCBs at a low cost and have promotions and coupons available throughout the year. You can sign up using here, or using the following link:
https://jlcpcb.com/?from=Nerd that will support me as a creator to keep making content that is accessible and open source at no charge to you.
Ordering the PCB is very simple:
Download the Gerber file here.
Click on Add Gerber file
leave all the settings as default given. You might want change the PCB color which you can do here:
Enter you shipping details, save to cart
Then after a few days depending on your location you will receive your great quality PCB.
Enclosure Design:
The enclosure here is a simple draft that was quickly made and a better version will be done later. If you make your own enclosure please share it with me and I can upload it here.
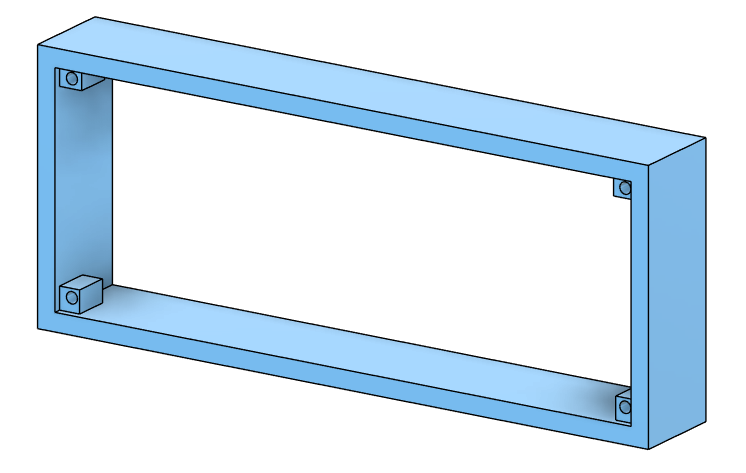
Download STL file here: download.
Code
You are going to need 4 files for this project
- config.json: In this file we will store all our private information, Wifi-Password, API Key and our city and country code.
- ssd1306.py: The library for controlling the ssd1306 OLED display
- urequests.py: Connecting the Pico W to the internet to use API to collect data
- main.py: The main program that will run on boot when the Pico is powered.
You can download the code using the following link, or copy it from this webpage below.
config.json
{
"ssid": "Open_Internet",
"ssid_password": "25802580",
"query_interval_sec": 120,
"weather_api_key": "ce54c4b03cfc0bd0fc037188def2d98e",
"city": "Qingdao",
"country_code": "CN",
"date_time_api": "01bf0795f82e4e37bdd6fa163525131e",
"time_zone": "Asia/Shanghai",
}
ssd1306.py
# MicroPython SSD1306 OLED driver, I2C and SPI interfaces
from micropython import const
import framebuf
# register definitions
SET_CONTRAST = const(0x81)
SET_ENTIRE_ON = const(0xA4)
SET_NORM_INV = const(0xA6)
SET_DISP = const(0xAE)
SET_MEM_ADDR = const(0x20)
SET_COL_ADDR = const(0x21)
SET_PAGE_ADDR = const(0x22)
SET_DISP_START_LINE = const(0x40)
SET_SEG_REMAP = const(0xA0)
SET_MUX_RATIO = const(0xA8)
SET_IREF_SELECT = const(0xAD)
SET_COM_OUT_DIR = const(0xC0)
SET_DISP_OFFSET = const(0xD3)
SET_COM_PIN_CFG = const(0xDA)
SET_DISP_CLK_DIV = const(0xD5)
SET_PRECHARGE = const(0xD9)
SET_VCOM_DESEL = const(0xDB)
SET_CHARGE_PUMP = const(0x8D)
# Subclassing FrameBuffer provides support for graphics primitives
# http://docs.micropython.org/en/latest/pyboard/library/framebuf.html
class SSD1306(framebuf.FrameBuffer):
def __init__(self, width, height, external_vcc):
self.width = width
self.height = height
self.external_vcc = external_vcc
self.pages = self.height // 8
self.buffer = bytearray(self.pages * self.width)
super().__init__(self.buffer, self.width, self.height, framebuf.MONO_VLSB)
self.init_display()
def init_display(self):
for cmd in (
SET_DISP, # display off
# address setting
SET_MEM_ADDR,
0x00, # horizontal
# resolution and layout
SET_DISP_START_LINE, # start at line 0
SET_SEG_REMAP | 0x01, # column addr 127 mapped to SEG0
SET_MUX_RATIO,
self.height - 1,
SET_COM_OUT_DIR | 0x08, # scan from COM[N] to COM0
SET_DISP_OFFSET,
0x00,
SET_COM_PIN_CFG,
0x02 if self.width > 2 * self.height else 0x12,
# timing and driving scheme
SET_DISP_CLK_DIV,
0x80,
SET_PRECHARGE,
0x22 if self.external_vcc else 0xF1,
SET_VCOM_DESEL,
0x30, # 0.83*Vcc
# display
SET_CONTRAST,
0xFF, # maximum
SET_ENTIRE_ON, # output follows RAM contents
SET_NORM_INV, # not inverted
SET_IREF_SELECT,
0x30, # enable internal IREF during display on
# charge pump
SET_CHARGE_PUMP,
0x10 if self.external_vcc else 0x14,
SET_DISP | 0x01, # display on
): # on
self.write_cmd(cmd)
self.fill(0)
self.show()
def poweroff(self):
self.write_cmd(SET_DISP)
def poweron(self):
self.write_cmd(SET_DISP | 0x01)
def contrast(self, contrast):
self.write_cmd(SET_CONTRAST)
self.write_cmd(contrast)
def invert(self, invert):
self.write_cmd(SET_NORM_INV | (invert & 1))
def rotate(self, rotate):
self.write_cmd(SET_COM_OUT_DIR | ((rotate & 1) << 3))
self.write_cmd(SET_SEG_REMAP | (rotate & 1))
def show(self):
x0 = 0
x1 = self.width - 1
if self.width != 128:
# narrow displays use centred columns
col_offset = (128 - self.width) // 2
x0 += col_offset
x1 += col_offset
self.write_cmd(SET_COL_ADDR)
self.write_cmd(x0)
self.write_cmd(x1)
self.write_cmd(SET_PAGE_ADDR)
self.write_cmd(0)
self.write_cmd(self.pages - 1)
self.write_data(self.buffer)
class SSD1306_I2C(SSD1306):
def __init__(self, width, height, i2c, addr=0x3C, external_vcc=False):
self.i2c = i2c
self.addr = addr
self.temp = bytearray(2)
self.write_list = [b"\x40", None] # Co=0, D/C#=1
super().__init__(width, height, external_vcc)
def write_cmd(self, cmd):
self.temp[0] = 0x80 # Co=1, D/C#=0
self.temp[1] = cmd
self.i2c.writeto(self.addr, self.temp)
def write_data(self, buf):
self.write_list[1] = buf
self.i2c.writevto(self.addr, self.write_list)
class SSD1306_SPI(SSD1306):
def __init__(self, width, height, spi, dc, res, cs, external_vcc=False):
self.rate = 10 * 1024 * 1024
dc.init(dc.OUT, value=0)
res.init(res.OUT, value=0)
cs.init(cs.OUT, value=1)
self.spi = spi
self.dc = dc
self.res = res
self.cs = cs
import time
self.res(1)
time.sleep_ms(1)
self.res(0)
time.sleep_ms(10)
self.res(1)
super().__init__(width, height, external_vcc)
def write_cmd(self, cmd):
self.spi.init(baudrate=self.rate, polarity=0, phase=0)
self.cs(1)
self.dc(0)
self.cs(0)
self.spi.write(bytearray([cmd]))
self.cs(1)
def write_data(self, buf):
self.spi.init(baudrate=self.rate, polarity=0, phase=0)
self.cs(1)
self.dc(1)
self.cs(0)
self.spi.write(buf)
self.cs(1)
urequests.py
import usocket
class Response:
def __init__(self, f):
self.raw = f
self.encoding = "utf-8"
self._cached = None
def close(self):
if self.raw:
self.raw.close()
self.raw = None
self._cached = None
@property
def content(self):
if self._cached is None:
try:
self._cached = self.raw.read()
finally:
self.raw.close()
self.raw = None
return self._cached
@property
def text(self):
return str(self.content, self.encoding)
def json(self):
import ujson
return ujson.loads(self.content)
def request(method, url, data=None, json=None, headers={}, stream=None):
try:
proto, dummy, host, path = url.split("/", 3)
except ValueError:
proto, dummy, host = url.split("/", 2)
path = ""
if proto == "http:":
port = 80
elif proto == "https:":
import ussl
port = 443
else:
raise ValueError("Unsupported protocol: " + proto)
if ":" in host:
host, port = host.split(":", 1)
port = int(port)
ai = usocket.getaddrinfo(host, port, 0, usocket.SOCK_STREAM)
try:
ai = ai[0]
except:
print("Count not resolve getaddrinfo for {} {}".format(host,port))
s = usocket.socket(ai[0], ai[1], ai[2])
try:
s.connect(ai[-1])
if proto == "https:":
s = ussl.wrap_socket(s, server_hostname=host)
s.write(b"%s /%s HTTP/1.0\r\n" % (method, path))
if not "Host" in headers:
s.write(b"Host: %s\r\n" % host)
# Iterate over keys to avoid tuple alloc
for k in headers:
s.write(k)
s.write(b": ")
s.write(headers[k])
s.write(b"\r\n")
if json is not None:
assert data is None
import ujson
data = ujson.dumps(json)
s.write(b"Content-Type: application/json\r\n")
if data:
s.write(b"Content-Length: %d\r\n" % len(data))
s.write(b"\r\n")
if data:
s.write(data)
l = s.readline()
#print(l)
l = l.split(None, 2)
status = int(l[1])
reason = ""
if len(l) > 2:
reason = l[2].rstrip()
while True:
l = s.readline()
if not l or l == b"\r\n":
break
#print(l)
if l.startswith(b"Transfer-Encoding:"):
if b"chunked" in l:
raise ValueError("Unsupported " + l)
elif l.startswith(b"Location:") and not 200 <= status <= 299:
raise NotImplementedError("Redirects not yet supported")
except OSError:
s.close()
raise
resp = Response(s)
resp.status_code = status
resp.reason = reason
return resp
def head(url, **kw):
return request("HEAD", url, **kw)
def get(url, **kw):
return request("GET", url, **kw)
def post(url, **kw):
return request("POST", url, **kw)
def put(url, **kw):
return request("PUT", url, **kw)
def patch(url, **kw):
return request("PATCH", url, **kw)
def delete(url, **kw):
return request("DELETE", url, **kw)
main.py
import utime
from machine import Pin, I2C, RTC
import json
import urequests
import network
from ssd1306 import SSD1306_I2C
from neopixel import Neopixel
# ============================
# NeoPixel Setup (20 LEDs)
# ============================
NUM_LEDS = 20
PIN_NUM = 0
STATE_MACHINE = 0
np = Neopixel(NUM_LEDS, STATE_MACHINE, PIN_NUM, "GRB")
np.brightness(80) # optional: 1-255
# Time colors (EDIT THESE ANYTIME)
# NOTE: Your tuple format is (R, G, B) — library handles GRB packing internally
COLOR_HOURS = (255, 0, 0) # Red
COLOR_MINUTES = (0, 0, 255) # Blue
COLOR_SECONDS = (0, 180, 180) # Cyan-ish
def all_off():
np.clear()
np.show()
# LED Groups: start index or custom list
groups = {
"H_tens": (0, 2),
"H_ones": (2, 4),
"M_tens": (6, 3),
"M_ones": (9, 4),
"S_tens": (13, 3),
"S_ones": (16, 4),
}
# LSB first + supports custom lists
def set_group_value(group, length, value, color):
if isinstance(group, list):
for i in range(length):
bit = (value >> i) & 1
np.set_pixel(group[i], color if bit else (0, 0, 0))
else:
start = group
for i in range(length):
bit = (value >> i) & 1
np.set_pixel(start + i, color if bit else (0, 0, 0))
def update_leds_ws2812():
Y, M, D, W, H, Min, S, SS = rtc.datetime()
h1, h2 = divmod(H, 10)
m1, m2 = divmod(Min, 10)
s1, s2 = divmod(S, 10)
set_group_value(*groups["H_tens"], h1, COLOR_HOURS)
set_group_value(*groups["H_ones"], h2, COLOR_HOURS)
set_group_value(*groups["M_tens"], m1, COLOR_MINUTES)
set_group_value(*groups["M_ones"], m2, COLOR_MINUTES)
set_group_value(*groups["S_tens"], s1, COLOR_SECONDS)
set_group_value(*groups["S_ones"], s2, COLOR_SECONDS)
np.show()
# ============================
# WiFi + API + RTC + OLED
# ============================
with open('config.json') as f:
config = json.load(f)
if config['ssid'] == 'Enter_Wifi_SSID':
raise ValueError("config.json not updated")
weather_api_key = config['weather_api_key']
city = config['city']
country_code = config['country_code']
date_time_api = config['date_time_api']
timezone = config['time_zone']
# WiFi Init
wlan = network.WLAN(network.STA_IF)
wlan.active(True)
print("Connecting to WiFi:", config['ssid'])
wlan.connect(config['ssid'], config['ssid_password'])
while not wlan.isconnected():
utime.sleep(1)
print("Connected:", wlan.ifconfig())
rtc = RTC()
def sync_time_with_ip_geolocation_api(rtc):
try:
url = f'http://api.ipgeolocation.io/timezone?apiKey={date_time_api}&tz={timezone}'
r = urequests.get(url)
d = r.json()
r.close()
date, t = d["date_time"].split(" ")
y, m, day = map(int, date.split("-"))
h, mi, s = map(int, t.split(":"))
wd = d.get("day_of_week", 0)
rtc.datetime((y, m, day, wd, h, mi, s, 0))
return True
except:
return False
def fetch_weather():
try:
url = f"http://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather?q={city},{country_code}&appid={weather_api_key}&units=metric"
r = urequests.get(url)
d = r.json()
r.close()
return {
'location': f"{d['name']} - {d['sys']['country']}",
'description': d['weather'][0]['main'],
'temperature': d['main']['temp'],
'pressure': d['main']['pressure'],
'humidity': d['main']['humidity'],
'wind_speed': d['wind']['speed'],
}
except:
return None
# OLED Setup
i2c = I2C(0, scl=Pin(17), sda=Pin(16), freq=400000)
display = SSD1306_I2C(128, 64, i2c)
def show_status(msg, line=0):
display.fill(0)
display.text("NerdCave Clock", 0, 0)
display.text(msg, 0, 20 + line*12)
display.show()
# Buttons
btn_next = Pin(11, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
btn_prev = Pin(12, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
current_page = 0
total_pages = 3
def handle_buttons():
global current_page
if btn_next.value():
current_page = (current_page + 1) % total_pages
utime.sleep_ms(250)
if btn_prev.value():
current_page = (current_page - 1) % total_pages
utime.sleep_ms(250)
# OLED Pages
def display_time_date():
Y, M, D, W, H, Min, S, SS = rtc.datetime()
display.fill(0)
display.text("NerdCave Clock", 0, 0)
display.text(f"{D:02}-{M:02}-{Y}", 0, 20)
display.text(f"{H:02}:{Min:02}:{S:02}", 0, 35)
display.show()
def display_weather_basic(w):
display.fill(0)
display.text("Weather:", 0, 0)
display.text(w['location'], 0, 12)
display.text(f"T:{w['temperature']}C", 0, 24)
display.text(w['description'], 0, 36)
display.text(f"H:{w['humidity']}%", 0, 48)
display.show()
def display_weather_extended(w):
display.fill(0)
display.text("Weather Ext:", 0, 0)
display.text(f"P:{w['pressure']}", 0, 16)
display.text(f"W:{w['wind_speed']}m/s", 0, 32)
display.text(f"T:{w['temperature']}C", 0, 48)
display.show()
# Startup
show_status("WiFi OK")
w = fetch_weather()
show_status("Weather OK" if w else "Weather ERR")
show_status("Time OK" if sync_time_with_ip_geolocation_api(rtc) else "Time ERR", 1)
# Optional: clear LEDs on boot
all_off()
# Main Loop
last_weather_update = utime.time()
last_time_sync = utime.time()
last_tick = utime.ticks_ms()
while True:
if utime.ticks_diff(utime.ticks_ms(), last_tick) >= 1000:
last_tick = utime.ticks_ms()
handle_buttons()
update_leds_ws2812()
if current_page == 0:
display_time_date()
elif current_page == 1 and w:
display_weather_basic(w)
elif current_page == 2 and w:
display_weather_extended(w)
if utime.time() - last_weather_update > 600:
w = fetch_weather()
last_weather_update = utime.time()
if utime.time() - last_time_sync > 600:
sync_time_with_ip_geolocation_api(rtc)
last_time_sync = utime.time()
Conclusion
Hope you enjoy this project.