Tutorial 4- Matrix Keypad
In this tutorial, we will learn how to connect a matrix keypad to the Raspberry Pi 5 and receive the input characters.
Introduction
A keypad is a rectangular array of buttons. In this tutorial, we’ll learn how to connect a matrix keypad to the Raspberry Pi 5 board. We’ll write a Micropython program that reads the different character inputs.
Components Needed
| Component | Quantity |
|---|---|
| Raspberry Pi 5 | 1 |
| Breadboard | 1 |
| Wires | Several |
| Matrix Keypad | 1 |
| 1K Ohm Resistor | 8 |
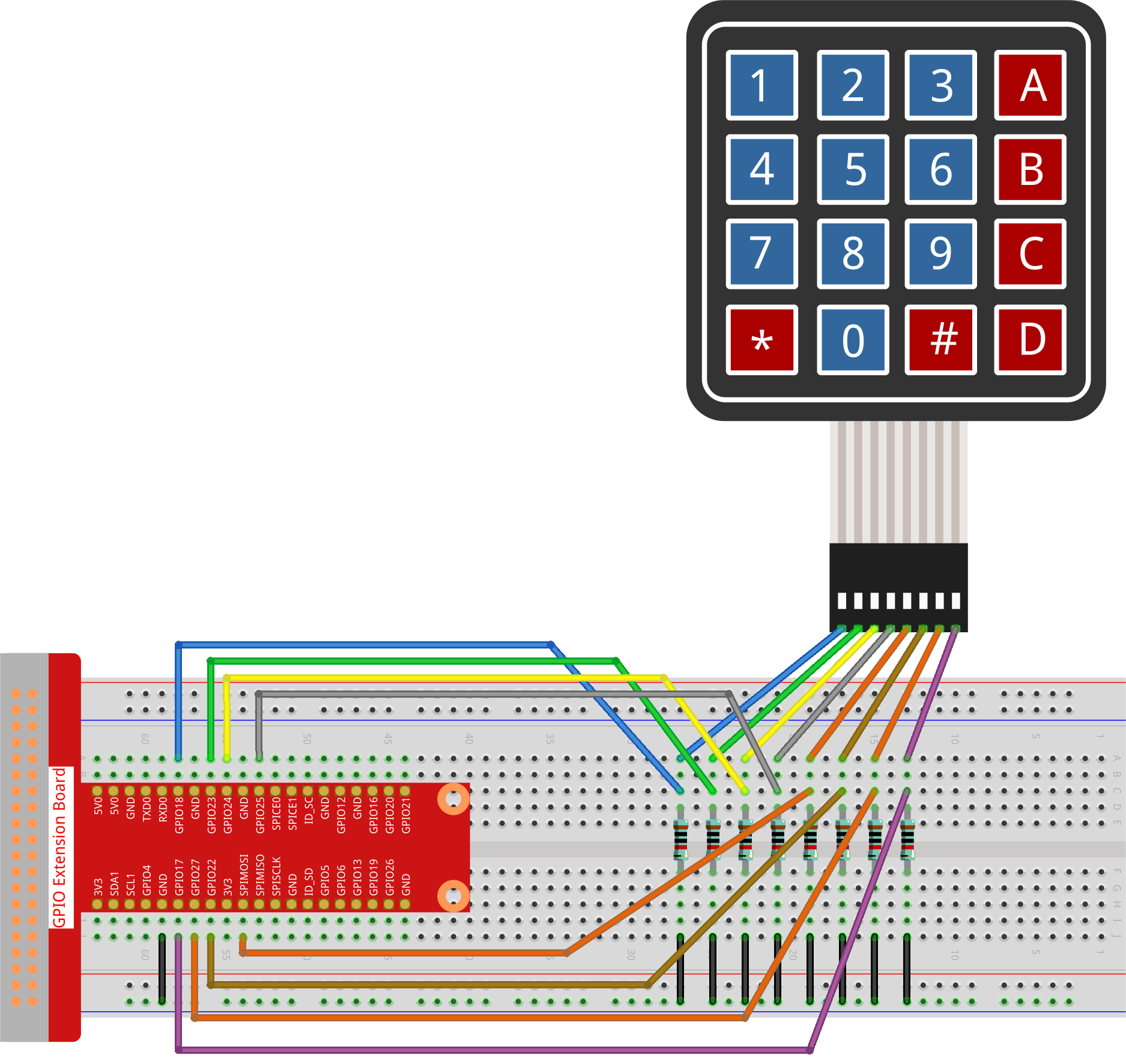
Fritzing Diagram
Connect the Keypad to your Raspberry Pi as shown in the following diagram.
Code
from gpiozero import DigitalOutputDevice, Button
from time import sleep
# Configure rows, columns, and keypad layout
rows_pins = [18, 23, 24, 25]
cols_pins = [10, 22, 27, 17]
keys = ["1", "2", "3", "A",
"4", "5", "6", "B",
"7", "8", "9", "C",
"*", "0", "#", "D"]
# Initialize row pins as DigitalOutputDevice
rows = [DigitalOutputDevice(pin) for pin in rows_pins]
# Initialize column pins as Buttons
cols = [Button(pin, pull_up=False) for pin in cols_pins]
def read_keypad():
"""
Read the currently pressed keys on the keypad.
:return: A list of pressed keys.
"""
pressed_keys = []
# Scan each row and column to identify pressed keys
for i, row in enumerate(rows):
row.on() # Enable the current row
for j, col in enumerate(cols):
if col.is_pressed: # Check if the column button is pressed
# Calculate the key index based on row and column
index = i * len(cols) + j
pressed_keys.append(keys[index])
row.off() # Disable the current row
return pressed_keys
# Main loop to continuously read the keypad and print newly pressed keys
last_key_pressed = []
print("Press keys on the keypad. Press Ctrl+C to exit.")
while True:
pressed_keys = read_keypad()
if pressed_keys and pressed_keys != last_key_pressed:
print(pressed_keys) # Print the list of pressed keys
last_key_pressed = pressed_keys
sleep(0.1) # Short delay to reduce CPU load
Code Overview
Initialization: The rows and columns are initialized as lists of DigitalOutputDevice and Button objects, respectively, outside any class.
Function read_keypad(): This function scans the keypad for pressed keys, similar to the previous class method, and returns a list of pressed keys.
Main Loop: The main loop continuously calls the read_keypad() function to check for pressed keys and prints them if they differ from the last recorded keys.
No Class Structure: The code is now simpler and does not use classes, making it straightforward for basic usage.
Code Explanation
Imports and Setup
from gpiozero import DigitalOutputDevice, Button
from time import sleep
# Configure rows, columns, and keypad layout
rows_pins = [18, 23, 24, 25]
cols_pins = [10, 22, 27, 17]
keys = ["1", "2", "3", "A", "4", "5", "6", "B", "7", "8", "9", "C", "*", "0", "#", "D"]
# Initialize row pins as DigitalOutputDevice
rows = [DigitalOutputDevice(pin) for pin in rows_pins]
# Initialize column pins as Buttons
cols = [Button(pin, pull_up=False) for pin in cols_pins]
Imports: The necessary classes from the gpiozero library are imported.
Pin Configuration: GPIO pins for rows and columns are defined, along with the keypad layout.
Initialization: Row pins are set as DigitalOutputDevice, and column pins are set as Button instances.
Keypad Reading Function
def read_keypad():
pressed_keys = []
for i, row in enumerate(rows):
row.on() # Enable the current row
for j, col in enumerate(cols):
if col.is_pressed: # Check if the column button is pressed
index = i * len(cols) + j # Calculate the key index
pressed_keys.append(keys[index]) # Append the pressed key
row.off() # Disable the current row
return pressed_keys
Function Definition: read_keypad() scans the keypad to check which keys are pressed.
Row and Column Scanning: Each row is activated in turn, and the corresponding columns are checked for button presses.
Key Index Calculation: The index of the pressed key is calculated based on the active row and column, and the key is added to the pressed_keys list.
Main Loop
last_key_pressed = []
print("Press keys on the keypad. Press Ctrl+C to exit.")
while True:
pressed_keys = read_keypad() # Read current pressed keys
if pressed_keys and pressed_keys != last_key_pressed:
print(pressed_keys) # Print newly pressed keys
last_key_pressed = pressed_keys # Update last pressed keys
sleep(0.1) # Short delay to reduce CPU load
Last Key Tracking: A list last_key_pressed is initialized to keep track of the last detected keys.
Continuous Loop: The program enters an infinite loop to continuously read the keypad.
Key Printing: If new keys are detected, they are printed, and the last pressed keys list is updated.
CPU Load Management: A brief sleep of 0.1 seconds is included to reduce CPU usage.
Conclusion
This code initializes a keypad using GPIO pins, continuously reads the pressed keys, and prints them to the console. The structure is straightforward, making it easy to understand and modify for basic keypad functionality.
Code Password Example
from gpiozero import DigitalOutputDevice, Button
from time import sleep
# Configure rows, columns, and keypad layout
rows_pins = [18, 23, 24, 25]
cols_pins = [10, 22, 27, 17]
keys = ["1", "2", "3", "A",
"4", "5", "6", "B",
"7", "8", "9", "C",
"*", "0", "#", "D"]
# Initialize row pins as DigitalOutputDevice
rows = [DigitalOutputDevice(pin) for pin in rows_pins]
# Initialize column pins as Buttons
cols = [Button(pin, pull_up=False) for pin in cols_pins]
# Define the secret password
password = ["1", "2", "3", "4"] # Example password
entered_keys = [] # List to store entered keys
def read_keypad():
"""
Read the currently pressed keys on the keypad.
:return: A list of pressed keys.
"""
pressed_keys = []
# Scan each row and column to identify pressed keys
for i, row in enumerate(rows):
row.on() # Enable the current row
for j, col in enumerate(cols):
if col.is_pressed: # Check if the column button is pressed
# Calculate the key index based on row and column
index = i * len(cols) + j
pressed_keys.append(keys[index])
row.off() # Disable the current row
return pressed_keys
# Main loop to continuously read the keypad and check for password entry
last_key_pressed = []
print("Press keys on the keypad. Press Ctrl+C to exit.")
while True:
pressed_keys = read_keypad()
if pressed_keys and pressed_keys != last_key_pressed:
for key in pressed_keys:
if key == "#": # Assuming "#" is used to submit the password
if entered_keys == password:
print("Access Granted!")
else:
print("Access Denied! Try again.")
entered_keys = [] # Clear the entered keys after submission
elif key == "*": # Assuming "*" is used to clear the entry
entered_keys = [] # Clear the entered keys
else:
entered_keys.append(key) # Add the key to the entered keys
print(f"Entered keys: {entered_keys}") # Print currently entered keys
last_key_pressed = pressed_keys
sleep(0.1) # Short delay to reduce CPU load